Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakano, Hiroko; Fujinami, Kyoko; Yamaura, Takayuki; Kawakami, Jun; Hanakawa, Hiroki
JAEA-Review 2023-036, 33 Pages, 2024/03
A practical training course using the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) and other research infrastructures was held from November 29 to December 2 in 2021 for Asian young researchers and engineers. This course was adopted as International Youth Exchange Program in Science (SAKURA SCIENCE Exchange Program) which is the project of the Japan Science and Technology Agency, and this course aims to enlarge the number of high-level nuclear researchers/engineers in Asian countries which are planning to introduce a nuclear power plant, and to promote the use of facilities in future. In this year, from the viewpoint of preventing the spread of COVID-19 infection, it was decided to hold the event online. 53 young researchers and engineers joined the course from 6 countries. In FY2022, training programs with invitations were held due to the easing of restrictions on entry into Japan from overseas. 7 young researchers and engineers from4 Asian countries participated in the training from February 1 to 10, 2023.The common curriculum in the training course of FY2021 and FY2022 included lectures on nuclear energy, irradiation testing, safety management, JMTR decommissioning plan, etc. In the online session, conducted in FY2021, information exchange on the energy situation in each country was conducted. On-site training conducted in FY2022, included practical training on operation using simulations, environmental monitoring, etc. and facility tours of the JMTR, etc. Many participants could join the online training course, they created a diversity of expertise and made lively discussions during the information exchange. On-site training, while limited in number of participants, provided a good opportunity for personnel exchange through practical training and face-face communication. It is desirable to hold on-site training as long as circumstances permit. This report summarizes the training conducted in FY2021 and FY2022.
Takayama, Yusuke; Yamamoto, Yoichi*; Goto, Takahiro*
Jiban Kogaku Janaru (Internet), 18(3), p.317 - 330, 2023/09
It has been reported that the deformation greatly increased in the secondary consolidation process in the past long-term consolidation test of 1.8 years on Na-type bentonite/sand mixed soil. Therefore, we analyzed potential contributing factors in this behavior. A long-term consolidation test for about 10 years on bentonite and kaolinite was started using the test equipment with countermeasures against these factors. In this paper, the secondary consolidation behavior of bentonite was investigated based on the long-term consolidation test data for 2.7, 3.7 and 4 years. The results were generally consistent with the conventional findings on soil mechanics that the deformation due to secondary consolidation progresses linearly with respect to logarithm of time. This test will be continued for about 10 years and longer-term secondary consolidation behavior will be investigated.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Shizukawa, Yuta; Tanno, Takashi; Imagawa, Yuya; Hashidate, Ryuta; Yano, Yasuhide; Onizawa, Takashi; Kaito, Takeji; Onuma, Masato*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.288 - 298, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:76.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has been developing 9Cr-oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) tempered martensitic steel(TMS) as a candidate material for the fuel cladding tubes of sodium-cooled fast reactors(SFRs). The reliable prediction of in-reactor creep-rupture strength is critical for implementing the 9Cr-ODS TMS cladding tube in the SFR. This study investigated the quantitative correlation between the creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700  C and the dispersions of nanosized oxides by analyzing the creep data and the material's nanostructure. The possibility of deriving a formula for estimating the in-reactor creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMSs based on an analysis of the nanostructure of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS TMSs was also discussed. The creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700
C and the dispersions of nanosized oxides by analyzing the creep data and the material's nanostructure. The possibility of deriving a formula for estimating the in-reactor creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMSs based on an analysis of the nanostructure of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS TMSs was also discussed. The creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700  C closely correlated with the dispersion of nanosized oxide particles. The correlation between creep-rupture lives and nanosized oxide particle dispersion was determined using existing creep models. The elucidation of correlation between the stress exponent of secondary creep rate and the nanostructure is essential to enhance future modeling reliability and formulation.
C closely correlated with the dispersion of nanosized oxide particles. The correlation between creep-rupture lives and nanosized oxide particle dispersion was determined using existing creep models. The elucidation of correlation between the stress exponent of secondary creep rate and the nanostructure is essential to enhance future modeling reliability and formulation.
Saito, Shigeru; Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Obata, Hiroki; Dai, Y.*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 34, p.101338_1 - 101338_9, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, a post-irradiation examination of pure tungsten (W) and tantalum (Ta) specimens irradiated at the Swiss Spallation-Neutron Source is conducted. W is used as a potential candidate for a solid spallation-target material owing to its favorable properties. However, W also suffers from several disadvantages such as poor corrosion resistance to water coolant and irradiation embrittlement. To improve these properties, cladding technologies using Ta for W alloys have been developed. In the present study, we investigated the irradiation effects on two tungsten materials, poly-crystal W (W-Poly) and single-crystal W (W-Sin), along with pure polycrystalline Ta. The tensile-test results revealed that W-Poly exhibited almost no ductility after irradiation of 10.2-35.0 dpa. W-Sin was irradiated up to 10.2 dpa and demonstrated 6% of total elongation (TE). With regard to Ta, TE decreased based on the increase in irradiation, reaching almost zero at doses of more than 10.3 dpa.
Yano, Yasuhide; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanno, Takashi; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of fast neutron irradiation on tensile properties of modified 316 stainless steel (PNC316) claddings and wrappers for fast reactors were investigated. PNC316 claddings and wrappers were irradiated in the experimental fast reactor Joyo at irradiation temperatures between 400 and 735  C to fast neutron doses ranging from 21 to 125 dpa. The post-irradiation tensile tests were carried out at room and irradiation temperatures. Elongations of PNC316 measured by the tensile tests were maintained at an engineering level, although the material incurred significant irradiation hardening and softening. The maximum swelling of PNC316 wrappers was about 2.5 vol.% at irradiation temperature between 400 and 500
C to fast neutron doses ranging from 21 to 125 dpa. The post-irradiation tensile tests were carried out at room and irradiation temperatures. Elongations of PNC316 measured by the tensile tests were maintained at an engineering level, although the material incurred significant irradiation hardening and softening. The maximum swelling of PNC316 wrappers was about 2.5 vol.% at irradiation temperature between 400 and 500 C up to 110 dpa. Japanese 20% cold-worked austenitic steels, PNC316 and 15Cr-20Ni, had sufficient ductility and work-hardenability even after above 10 vol.% swelling, while they had very weak plastic instabilities.
C up to 110 dpa. Japanese 20% cold-worked austenitic steels, PNC316 and 15Cr-20Ni, had sufficient ductility and work-hardenability even after above 10 vol.% swelling, while they had very weak plastic instabilities.
Oka, Hiroshi*; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 572, p.154032_1 - 154032_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:66.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)9Cr oxide dispersion strengthened steels with slightly different nitrogen concentrations (0.0034 - 0.029 wt%) were prepared and their creep property at 973 K was investigated with microstructural characterization before and after the creep test. The creep strength decreased significantly as the nitrogen concentration increased. Microstructural observation revealed that, in the higher nitrogen concentration specimen, coarse Y-rich inclusions were found along the boundary between transformed ferrite region and residual ferrite region. The solubility difference of nitrogen in  and
and  phase would induce the localized increment of nitrogen concentration in the boundary region during the austenitizing process, resulting in the thermodynamic destabilization and subsequent coarsening of the dispersed oxide particles. The rows of creep voids were found near the rupture part of the crept specimen, suggesting that the coarse inclusions were the starting point of creep void formation and the subsequent premature fracture.
phase would induce the localized increment of nitrogen concentration in the boundary region during the austenitizing process, resulting in the thermodynamic destabilization and subsequent coarsening of the dispersed oxide particles. The rows of creep voids were found near the rupture part of the crept specimen, suggesting that the coarse inclusions were the starting point of creep void formation and the subsequent premature fracture.
Doda, Norihiro; Yoshimura, Kazuo; Hamase, Erina; Yokoyama, Kenji; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of Technical Meeting on State-of-the-art Thermal Hydraulics of Fast Reactors (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/09
ARKADIA-Design is being developed to support the optimization of sodium-cooled fast reactors in the conceptual design stage. Design optimization requires various types of numerical analysis: 1-D plant dynamics analysis for efficient evaluation of various design options and multi-dimensional analysis for a detailed evaluation of local phenomena, including multi-physics. For those analyses, ARKADIA-Design performs whole plant analyses based on the multi-level simulation (MLS) technique in which the analysis codes are coupled to simulate the phenomena in an intended degree of resolution. This paper describes an outline of the coupling analysis methods in the MLS of the ARKADIA-Design and the numerical simulations of the experimental fast breeder reactor EBR-II tests by the coupled analysis.
Wakui, Takashi; Yamasaki, Kazuhiko*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Advanced Experimental Mechanics, 7, p.103 - 109, 2022/08
As part of the development of technique to cut and reduce the volume of highly radioactive components in the closed space, pulsed Nd:YAG laser was irradiated to radiation shielding glasses with the different lead content in the different irradiation condition; power and number of irradiation. The large black irradiated area with concave shape and cracks around it occurred with an increase of the lead content, power and number of irradiation. General mechanical properties in unirradiated and irradiated area were investigated to investigate the influence of mechanical properties on the irradiation damage. The thermal impact fracture toughness calculated based on the estimated mechanical properties decreased with increasing the lead content. The micro hardness in black irradiated area was 10% smaller than that in the unirradiated area. The change of the mechanical property due to the laser irradiation was confirmed.
Kurata, Masaki; Okuzumi, Naoaki*; Nakayoshi, Akira; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(7), p.807 - 834, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:96.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Immediately after the 1F-accident, various attempts have been made to evaluate the fuel debris characteristics toward the decommissioning of 1F. The present review outlines those attempts. In the years immediately following the 1F-accident, the knowledge obtained from the 1F-site (especially from the damaged reactors of Units 1, 2 and 3) was extremely limited. The approximate location of fuel debris was investigated by muon tomography, and its characteristics were roughly estimated based on the past findings such as the results of the Three Mile Island-II accident investigation in the United States, which gave us information of prototypical accident scenarios and debris characteristics for pressurized water reactor accident. After that, various internal investigation robots were developed, and from 2017, investigation of the inside of the reactor containment vessel was started using these robots. Consequently, these three units were found to have core damage status and debris distribution that were rather different from what had been expected based on the typical accident scenario of a pressurized water reactor. In parallel, a small amount of U-bearing particle was recovered from the smear samples of these robots. The analysis of these particles is ongoing to get information relevant to fuel debrsi body. Furthermore, international collaboration is ongoing mainly under OECD/NEA, including accident analysis and debris characterization. From now on, one need to further understand 1F-accident scenario and progress debris characterization based on these 1F-site information.
 /4H-SiC(11
/4H-SiC(11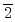 0) interfaces
0) interfacesNakanuma, Takato*; Iwakata, Yu*; Watanabe, Arisa*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 61(SC), p.SC1065_1 - SC1065_8, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:75.56(Physics, Applied)Nitridation of SiO /4H-SiC(11
/4H-SiC(11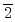 0) interfaces with post-oxidation annealing in an NO ambient (NO-POA) and its impact on the electrical properties were investigated. Sub-nm-resolution nitrogen depth profiling at the interfaces was conducted by using a scanning X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy microprobe. The results showed that nitrogen atoms were incorporated just at the interface and that interface nitridation proceeded much faster than at SiO
0) interfaces with post-oxidation annealing in an NO ambient (NO-POA) and its impact on the electrical properties were investigated. Sub-nm-resolution nitrogen depth profiling at the interfaces was conducted by using a scanning X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy microprobe. The results showed that nitrogen atoms were incorporated just at the interface and that interface nitridation proceeded much faster than at SiO /SiC(0001) interfaces, resulting in a 2.3 times higher nitrogen concentration. Electrical characterizations of metal-oxide-semiconductor capacitors were conducted through capacitance-voltage (
/SiC(0001) interfaces, resulting in a 2.3 times higher nitrogen concentration. Electrical characterizations of metal-oxide-semiconductor capacitors were conducted through capacitance-voltage (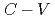 ) measurements in the dark and under illumination with ultraviolet light to evaluate the electrical defects near the conduction and valence band edges and those causing hysteresis and shifting of the
) measurements in the dark and under illumination with ultraviolet light to evaluate the electrical defects near the conduction and valence band edges and those causing hysteresis and shifting of the 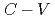 curves. While all of these defects were passivated with the progress of the interface nitridation, excessive nitridation resulted in degradation of the MOS capacitors. The optimal conditions for NO-POA are discussed on the basis of these experimental findings.
curves. While all of these defects were passivated with the progress of the interface nitridation, excessive nitridation resulted in degradation of the MOS capacitors. The optimal conditions for NO-POA are discussed on the basis of these experimental findings.
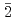 0) MOS devices
0) MOS devicesNakanuma, Takato*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 15(4), p.041002_1 - 041002_4, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:64.66(Physics, Applied)The leakage current and flat-band voltage (VFB) instability of NO-nitrided SiC (11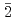 0) (a-face) MOS devices were systematically investigated. Although NO nitridation is effective in improving the interface properties, we found that it reduces the onset field of Fowler-Nordheim (F-N) current by about 1 MVcm
0) (a-face) MOS devices were systematically investigated. Although NO nitridation is effective in improving the interface properties, we found that it reduces the onset field of Fowler-Nordheim (F-N) current by about 1 MVcm , leading to pronounced leakage current. Synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that the nitridation reduces the conduction band offset at the SiO
, leading to pronounced leakage current. Synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that the nitridation reduces the conduction band offset at the SiO /SiC interface, corroborating the above finding. Furthermore, systematical positive and negative bias stress tests clearly indicated the VFB instability of nitrided a-face MOS devices against electron and hole injection.
/SiC interface, corroborating the above finding. Furthermore, systematical positive and negative bias stress tests clearly indicated the VFB instability of nitrided a-face MOS devices against electron and hole injection.
Doda, Norihiro; Hamase, Erina; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/04
In conventional design studies of sodium-cooled fast reactors, plant dynamics and local phenomena were evaluated separately by using simple models and detailed models, respectively, and their interaction was considered through the boundary conditions settings with conservativeness for each individual analysis. Thus, the final result through the analyses may contain excessive conservativeness. Therefore, JAEA began to develop a multi-level simulation system in which detailed analysis codes are coupled with a plant dynamics analysis code. Focusing on core thermal-hydraulics, a coupled analysis method using a plant dynamics analysis code Super-COPD and a subchannel analysis code ASFRE has been developed. The analysis on a test in the experimental fast reactor EBR-II was performed to validate the coupled analysis. Through the comparison of the analysis results and the measurement, it was confirmed that the coupled analysis could predict the transient temperature distribution in the subassembly, and the multi-level simulation by changing the level of detail in analysis model could be performed for core thermal-hydraulics.
Masaki, Nobuo*; Kato, Koji*; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Fujita, Satoshi*; Okamura, Shigeki*
Nihon Kenchiku Gakkai Gijutsu Hokokushu, 28(68), p.81 - 84, 2022/02
no abstracts in English
Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Oka, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 555, p.153105_1 - 153105_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.7(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The aim of this study was to evaluate the tensile properties and microstructures of dissimilar welds between 11Cr-ferritic/martensitic steel and 316 stainless steel after thermal aging at temperatures between 400 and 600 C up to 30,000 h. Characterization of microstructure was carried out by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Microstructural analysis showed that the microstructure in the weld metals consisted of lath martensite containing a small amount of residual austenite. Thermal aging hardening of WMs occurred at 400 and 450
C up to 30,000 h. Characterization of microstructure was carried out by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Microstructural analysis showed that the microstructure in the weld metals consisted of lath martensite containing a small amount of residual austenite. Thermal aging hardening of WMs occurred at 400 and 450 C due to the effects of both a-a' phase separation and G-phase precipitation. However, there was no significant change in the total elongation, and fracture surfaces indicated that very fine dimpled rupture was predominant rather than the cleavage rupture. It was suggested that lath martensite phases enhanced the tensile strength due to phase separation, while residual austenite played a role in keeping elongation as a soft phase.
C due to the effects of both a-a' phase separation and G-phase precipitation. However, there was no significant change in the total elongation, and fracture surfaces indicated that very fine dimpled rupture was predominant rather than the cleavage rupture. It was suggested that lath martensite phases enhanced the tensile strength due to phase separation, while residual austenite played a role in keeping elongation as a soft phase.
Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Ukai, Shigeharu*
Materials Transactions, 62(8), p.1239 - 1246, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The FeCrAl-ODS alloy claddings were manufactured and Vickers hardness, ring tensile tests and TEM observations of these claddings were performed to investigate the effects of thermal aging at 450  C for 5,000 and 15,000 h. The age-hardening of all FeCrAl-ODS alloy cladding was found. In addition, the significant increase in tensile strength was accompanied by much larger loss of ductility. It was suggested that this age-hardening behavior was attributed to the (Ti, Al)-enriched phase (
C for 5,000 and 15,000 h. The age-hardening of all FeCrAl-ODS alloy cladding was found. In addition, the significant increase in tensile strength was accompanied by much larger loss of ductility. It was suggested that this age-hardening behavior was attributed to the (Ti, Al)-enriched phase ( ' phase) and the
' phase) and the  ' phase precipitates (content of Al is
' phase precipitates (content of Al is  7 wt%). In comparison with FeCrAl-ODS alloys with almost same chemical compositions, there was significant age-hardening in both alloys. However, the extrusion bar with no-recrystallized structures was keeping good ductility. It was suggested that this different behavior of reduction ductility was attributed to the effects of grain boundaries, dislocation densities and specimen preparation direction.
7 wt%). In comparison with FeCrAl-ODS alloys with almost same chemical compositions, there was significant age-hardening in both alloys. However, the extrusion bar with no-recrystallized structures was keeping good ductility. It was suggested that this different behavior of reduction ductility was attributed to the effects of grain boundaries, dislocation densities and specimen preparation direction.
Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 4 Pages, 2021/05
For design optimization of fast reactors, in order to consider the feedback reactivity due to thermal deformation of the core when the core temperature rises, which could not be considered in the conventional design analysis, a neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structure mechanics coupled analysis method has been developed. Neutronics code, plant dynamics code, and structural mechanics code are coupled by a control module in python script. This paper outlines the coupling method of analysis codes and the results of its application to an experiment in an actual plant.
Sato, Hisashi*; Sawada, Atsushi; Takayama, Yusuke
JAEA-Research 2020-012, 37 Pages, 2020/11
In the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, it is important to fully understand the permeability and mass transport properties of actual fractures when setting parameters for permeability and mass transport properties of fractures. Permeability and mass transport properties of a fracture are affected by the void structure of the fracture. Therefore, it is necessary not only to conduct a hydraulic test but also to evaluate hydraulic properties based on the void structure of the fracture. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to develop a technique to acquire a three-dimensional void structure of a fracture from fracture surface shape data, and to obtain a dataset of three- dimensional void structure data and hydraulic data of the fracture. Specifically, we made a transparent replica sample of fracture and measure the fracture surface shape data in the exact coordinates. The three-dimensional void structure data was constituted from fracture surface shape data in the same coordinates. In addition, we conducted a permeability test and tracer test for the same sample to obtain a permeability and mass transport properties of the fracture. To assess the validity of the acquired data, we compared it with the apertures evaluated based on different methods. As a result, the average aperture from the fracture void structure was almost same as the average aperture acquired by different methods, from the above that the test result was validated.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-011, 50 Pages, 2020/11
This report summarize the results of the single borehole hydraulic test carried out at the -300 m Stage and the -500 m Stage of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory from FY 2016 to FY 2019. The details of each test (test interval depth, geology, etc.) as well as the interpreted hydraulic parameters and analytical methods used are presented in this report. Furthermore, the previous results of the single borehole hydraulic tests carried out in the Regional Hydrogeological Study Project and the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project before FY 2016 are also summarized in this report.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yamaguchi, Hisato*; Holby, E. F.*; Yamada, Takatoshi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 11(21), p.9159 - 9164, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.73(Chemistry, Physical)Atomically thin layers of graphene have been proposed to protect surfaces through the direct blocking of corrosion reactants such as oxygen with low added weight. The long term efficacy of such an approach, however, is unclear due to the long-term desired protection of decades and the presence of defects in as-synthesized materials. Here, we demonstrate catalytic permeation of oxygen molecules through previously-described impermeable graphene by imparting sub-eV kinetic energy to molecules. These molecules represent a small fraction of a thermal distribution thus this exposure serves as an accelerated stress test for understanding decades-long exposures. The permeation rate of the energized molecules increased 2 orders of magnitude compared to their non-energized counterpart. Graphene maintained its relative impermeability to non-energized oxygen molecules even after the permeation of energized molecules indicating that the process is non-destructive and a fundamental property of the exposed material.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Saito, Junichi; Daido, Hiroyuki*; Suemoto, Toru*
UVSOR-47, P. 85, 2020/08
To elucidate theoretically the transparent metallic sodium in the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) spectral range, the aim of this research is to obtain the accurate spectrum using UVSOR. We confirmed the validity for the transmittance measurement in UVSOR by the measurement of transmittance of CaF windows. However, the transparency phenomenon of VUV in the metallic sodium has never been confirmed by our group. In the future, we will improve the sodium sample and conduct the measurement again.
windows. However, the transparency phenomenon of VUV in the metallic sodium has never been confirmed by our group. In the future, we will improve the sodium sample and conduct the measurement again.